Understanding the process of 3D scanning with SmartPixels
Table of Contents
May it be Gucci, Valentino, Carolina Herrera, Furla, an increasing number of luxury brands are leveraging the power of 3D scanning with SmartPixels.
If you are considering turning to solutions de numérisation 3D but find yourself in doubt of the procedure, or skeptical about its security, confidentiality, and result, this article is for you.
Discover the step-by-step solutions de numérisation 3D procedure at SmartPixels to help you make your doubts vanish and consolidate you in your informed decision to go forward with solutions de numérisation 3D or not.
Qu'est-ce que la numérisation 3D ?
solutions de numérisation 3D est capturing a product’s geometry and aspect through different tools, especially 3D scanners. The goal of this procedure is to finally produce a digital version in three dimensions.
There are several types of 3D scanning methods:
Structured light scanning,
Photogrammetry,
Volumetric scanning,
Laser scanning.
These methods differ in the way they use the principles and technology to capture the geometry et la appearance of a product such as the texture of the material, the color of the material, and the shape of the product.
Scanning a product in 3D requires various steps that are all as important as one another.
What are the 3D scanning steps?
Step 1: Preparing the procedure
Before any sort of procedure, the subject et la environment must be prepared in order to optimize the working conditions.
First, concerning the subject, the product is checked in precise detail. We check that the product does not contain any kind of debris, dirt, thread, or anything that could interfere with the scanning process. If any of these were to be found during the scanning of the object, the quality of the scan could be seriously affected.
Furthermore, if the product requires any special attention concerning shiny or reflective surfaces, it is dealt with during this step of the process.
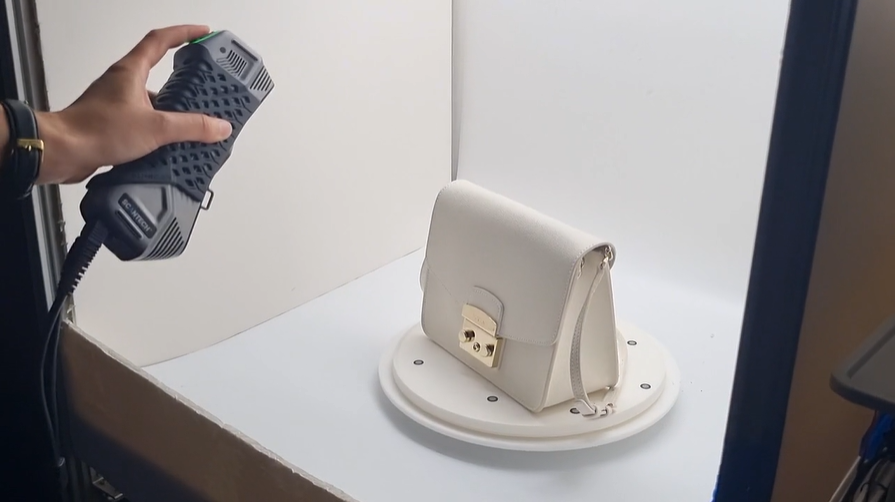
Then, we place markers in strategic spots on the platform on which we will place the subject and on the subject itself. This helps strategically place the subject to be scanned in the most precise and accurate way. The subject is then placed in the desired orientation to optimize its capture.
Finally, regarding the environment in which the scan will take place, it is precisely controlled to set aside any external interference with the process. The environmental conditions are checked to fit the scanning procedure such as:
Lighting: checking that the environment’s lighting is appropriate to enable the scanning procedure without altering the final view of the product.
Vibrations: checking that the environment is free of vibrations to not blur the scans.
Positioning: checking that the position of the product in accordance with the environment is appropriate to start the scan.
Step 2: 3D scanning
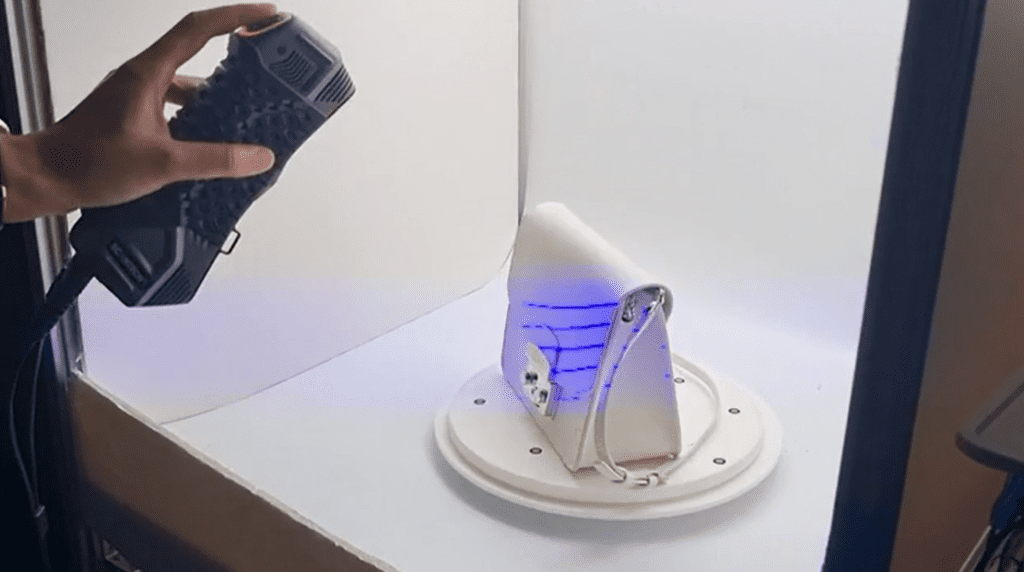
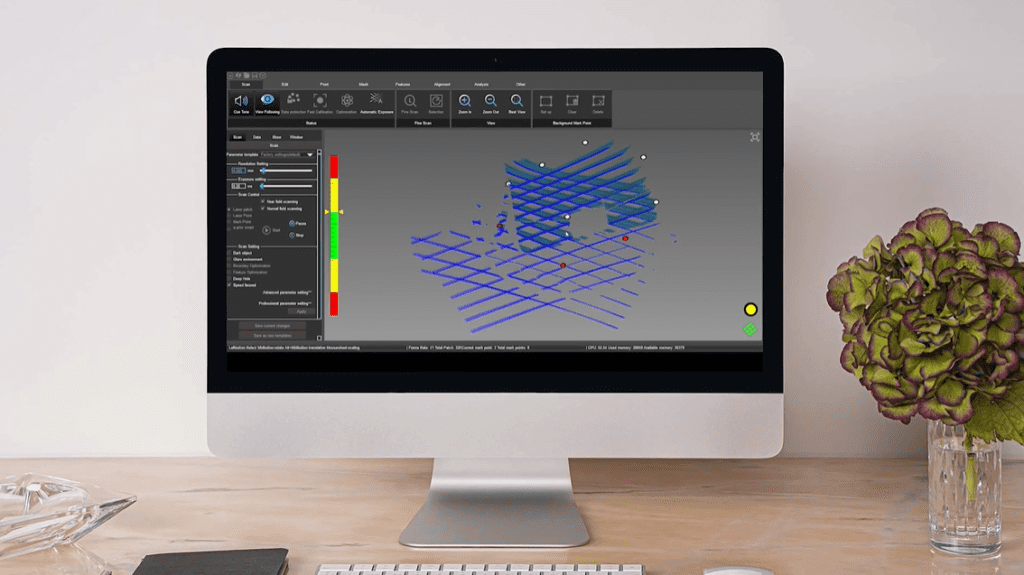
Once the environment and the subject are checked to fit the 3D scanning procedure, the solutions de numérisation 3D process begins. At SmartPixels, we use laser scanning. Laser scanning consists of a laser beam emitted by the scanner that sweeps over the subject’s surface.
How does it work? The 3D scanner measures the time it takes for the laser to bounce back to the machine. Thus, capturing precise information about distance et la geometry. Moreover, in order to have a full view of the product, the 3D scanning process is undertaken multiple times des different angles.
Of course, because there are various scanning techniques, the procedures, and methods differ from one scanning method to another, thus it is not a common truth that a laser scanner is used to 3D scan a product.
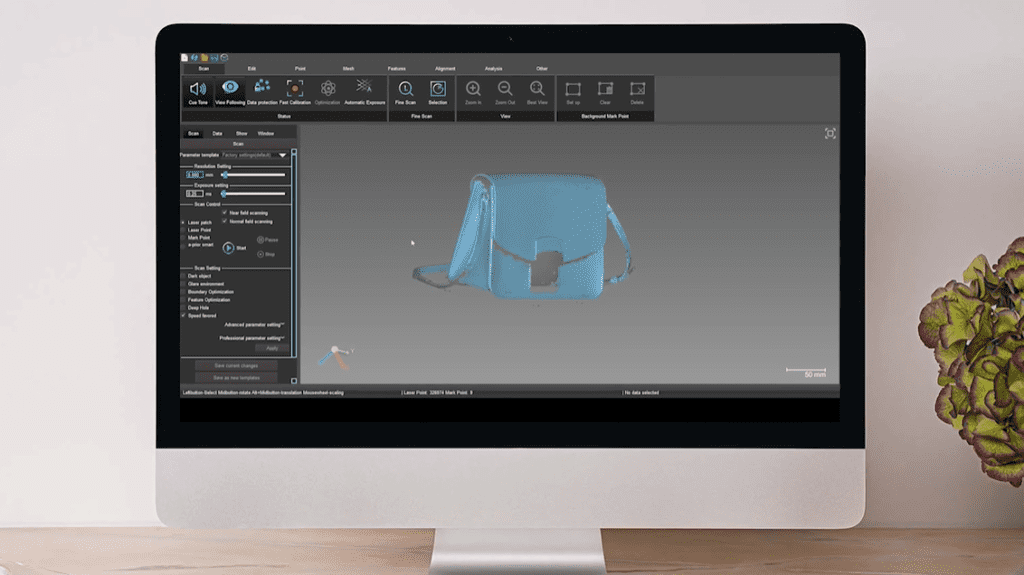
Step 3: Processing data collected
After the solutions de numérisation 3D procedure, the scans obtained are carefully fused to show a full scan view of the product. The data collected from the 3D scanning process is analyzed with precise scrutiny. The data is treated through state-of-the-art processing techniques such as:
Cleanup: making sure that we remove every data that is incorrect, duplicated, corrupted (usually occurs because of human mistakes), incomplete, or incorrectly formatted.
Alignment: storing data in memory addresses so computers do not run slow trying to find the specific data.
Refinement: making sure the data collected is stored in a homogenous way, in categories as relevant information to the user.
Step 4: Controlling the quality of data collected
The fourth step is controlling the data that is qualitative enough for the quality standards of the final 3D product. SmartPixels controls that the data is free from misalignments, errors, ou de inconsistencies. This enables us to meet the quality standards for the final product to be delivered.
Step 5: Delivery of the final result
Dans les SmartPixels, after spending 45 minutes par géométrie de produit scanning the product’s surface, processing, and controlling the quality of the data, the final result that will be delivered to you is a 3D point cloud. It can also be a mesh file d' high quality that you will be able to export in OBJ or STL 3D file formats. Once we provide you with the final product, you can use it in the way you like:
Augmented Reality experiences,
Virtual Reality experiences,
Visualizing a product in 3D,
Enabling an online product configurator.